Map:Iab75_6wu5u= Africa
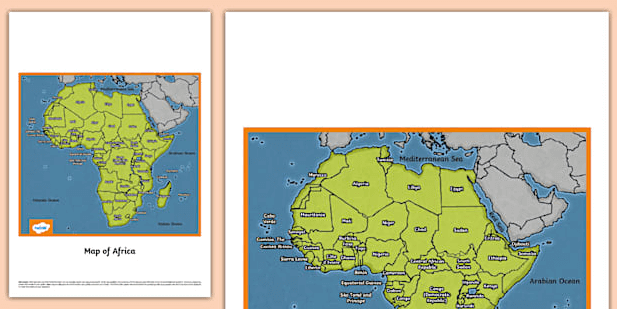
Map:Iab75_6wu5u= Africa serves as a crucial tool for understanding the continent’s intricate geographical and cultural tapestry. By illustrating key features such as the Atlas and Drakensberg mountains alongside vital river systems, it invites exploration of how these elements shape both the natural environment and human experiences. Furthermore, the depiction of significant cultural landmarks raises questions about the historical influences that have molded Africa’s socio-economic and political contexts. What implications do these geographical and cultural narratives hold for the future of the continent?
Overview of the Map
The map of Africa is frequently characterized by its diverse geographical features, political boundaries, and cultural landmarks, which collectively provide a comprehensive representation of the continent’s complexity.
Notably, topographic variations, including mountains, plains, and plateaus, are juxtaposed with distinct climate zones ranging from arid deserts to tropical rainforests.
This interplay of geography and climate informs regional development, biodiversity, and socio-economic dynamics across the continent.
Key Geographic Features
Africa’s landscape is marked by a multitude of geographic features that significantly influence its environmental and socio-economic contexts.
Prominent mountain ranges, such as the Atlas and the Drakensberg, create diverse climates and ecosystems. In contrast, extensive river systems like the Nile and the Congo facilitate trade and support agriculture.
Together, these elements shape the continent’s ecology and its people’s livelihoods.
Read also Logo:Sl-Fuh97cii= Brighton
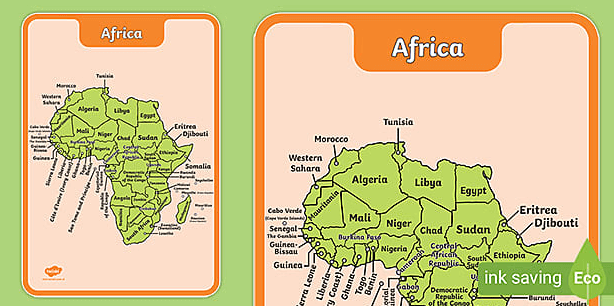
Cultural Landmarks Highlighted
Numerous cultural landmarks across the continent exemplify Africa’s rich heritage and diverse histories.
These sites encapsulate local traditions and reflect a variety of architectural styles, from ancient structures to modern creations.
Cultural festivals held at these landmarks showcase vibrant artistic expressions, fostering community engagement and preserving history.
Collectively, they serve as vital touchstones for understanding the continent’s multifaceted identity and cultural continuity.
Historical Significance and Context
Historical significance in Africa is deeply intertwined with the continent’s complex past, marked by ancient civilizations, colonial encounters, and post-colonial developments.
The colonial impact reshaped trade routes, redirecting commerce and altering socio-economic structures.
Understanding this context is essential for comprehending contemporary Africa, as historical legacies continue to influence political dynamics, cultural identities, and economic opportunities, ultimately shaping the quest for freedom and self-determination.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Map:Iab75_6wu5u= Africa serves as a compelling testament to the continent’s intricate interplay of geography, culture, and history. By illustrating the majestic Atlas and Drakensberg mountains alongside the vital Nile and Congo rivers, it encapsulates the essence of Africa’s diverse landscapes. Furthermore, the highlighted cultural landmarks evoke the echoes of ancient civilizations and colonial legacies, underscoring the ongoing narrative of resilience and transformation that continues to shape Africa’s socio-economic and political trajectories.






