0.0.0.0.1: A Comprehensive Guide for Network Administrators
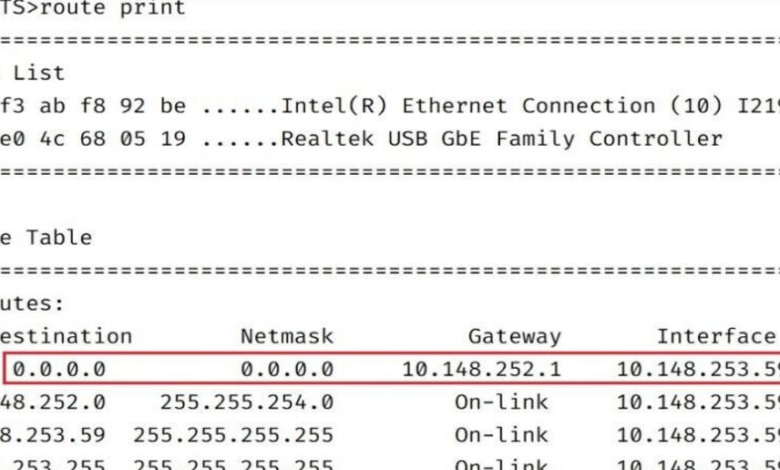
Network administrators often work with various IP addresses while managing and maintaining networks, each serving specific purposes. Among these, 0.0.0.0.1 stands out for its unique role and potential impact on network security and performance. While 0.0.0.0 typically denotes an unspecified IP or a default route in routing tables, 0.0.0.0.1 serves a different, less conventional purpose in network management. In this guide, we will break down the significance of 0.0.0.0.1 for network administrators, covering essential configurations, troubleshooting methods, and best practices to ensure this IP address is used effectively.
What is 0.0.0.0.1, and Why is it Important for Network Administration?
Understanding the 0.0.0.0.1 IP address is crucial for network administrators as it plays a specific role in network routing and management. Generally, 0.0.0.0 represents an unspecified IP address, often found in default routing scenarios or DHCP requests. When 0.0.0.0 appears in routing tables, it serves as a placeholder for any IP address not specified in the network’s routing protocols, effectively creating a “catch-all” route.
Recognizing 0.0.0.0 in Various Network Contexts
For network administrators, 0.0.0.0 appears in multiple contexts, from DHCP packets to ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) packets. In DHCP, 0.0.0.0 can identify a client that hasn’t received an IP from the server, useful in tracking IP allocations. In routing tables, 0.0.0.0 often represents a default path, while in OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), it might define area IDs.
Why 0.0.0.0.1 Can Indicate Misconfiguration
Unlike 0.0.0.0, 0.0.0.0.1 is not a recognized IP address for valid routing or network tasks. Its appearance usually flags misconfigured network settings or erroneous entries in the routing table, potentially causing connectivity issues. Recognizing this can help administrators address configuration errors that might compromise network stability.
How to Configure 0.0.0.0.1 for Network Security
Configuring 0.0.0.0.1 within network settings requires a clear understanding of IP routing and default gateways. Here’s how to ensure it’s set up correctly for a secure network.
Understanding Default Gateways and IP Addressing
Default gateways serve as access points between local networks and external systems or the internet, making them essential for routing information beyond the local network. In this context, 0.0.0.0 often indicates a default route, while 0.0.0.0.1 is less commonly used but may still appear in some configurations. When setting up 0.0.0.0 as a default route, it’s crucial to check the gateway settings for any misconfigured paths.
Steps to Configure 0.0.0.0.1 on Your Network
Access your router’s configuration panel, usually via a web interface or command-line tool, and set 0.0.0.0.1 only if your network demands specific configurations. Use the routing table to confirm the presence of 0.0.0.0 for all unassigned traffic and avoid setting 0.0.0.0.1 as it may create routing conflicts or misdirect traffic.

Can 0.0.0.0.1 Help Improve Network Performance?
While 0.0.0.0.1 isn’t typically associated with performance optimization, using 0.0.0.0 effectively can impact network speed and reliability. By understanding routing tables and addressing traffic paths, administrators can reduce latency and manage data flow efficiently.
Role of 0.0.0.0 in Reducing Latency
Using 0.0.0.0 as a default route ensures that any unassigned traffic is quickly directed to the proper gateway, minimizing potential delays. Proper configuration of 0.0.0.0 in routing tables can help improve network response times, as it reduces the processing time required to route traffic.
Network Routing and Traffic Management with 0.0.0.0
Setting 0.0.0.0 for unassigned traffic allows for efficient data tracking and flow management, preventing congestion on the network. Administrators should routinely review routing tables to ensure 0.0.0.0 directs traffic effectively, optimizing network performance and reliability.
Common Issues with 0.0.0.0.1 and How to Resolve Them
When using 0.0.0.0.1, administrators may encounter several issues, often stemming from misconfiguration or network conflicts. Here are some ways to address these problems.
Identifying IP Conflicts and Solutions
IP conflicts arise when multiple devices claim the same IP address. Network management tools can detect these conflicts, allowing administrators to quickly reassign IPs and maintain smooth communication across devices. Regular monitoring and correct DHCP configurations help minimize these conflicts.
Troubleshooting Connectivity Problems
Connectivity issues linked to 0.0.0.0.1 often result from routing or hardware misconfigurations. Use tools like `ping` and `tracert` to identify connection failures. Adjusting routing table settings and testing connections frequently helps resolve these issues promptly.
Security Vulnerabilities and Best Practices
Using 0.0.0.0.1 improperly can create security risks in network management. To avoid potential vulnerabilities, follow these security best practices.
Protecting Default Routes
Ensure that all default routes in your network configurations are secured to prevent unauthorized access. For instance, use firewalls to limit external access and prevent security breaches that might exploit default routes like 0.0.0.0.
Regular Security Assessments
Conduct regular assessments of your network configurations and routing tables. Confirm that routes like 0.0.0.0 are only used where necessary, limiting access to essential traffic paths. Security protocols like encrypted connections and strict firewall settings enhance network stability and safety.
Conclusion
Understanding and correctly managing 0.0.0.0.1 can make a significant difference in network performance and security. While this IP address may appear unconventional, it serves a crucial purpose when used appropriately. By following best practices, troubleshooting effectively, and maintaining up-to-date configurations, network administrators can ensure a secure and efficient network environment. Regular monitoring and adherence to security protocols help prevent common issues, making 0.0.0.0.1 a valuable asset in network management. With the insights from this guide, administrators can optimize 0.0.0.0.1 usage, supporting robust network operations.






