Latest Technology Updates on Thermal Interface Material
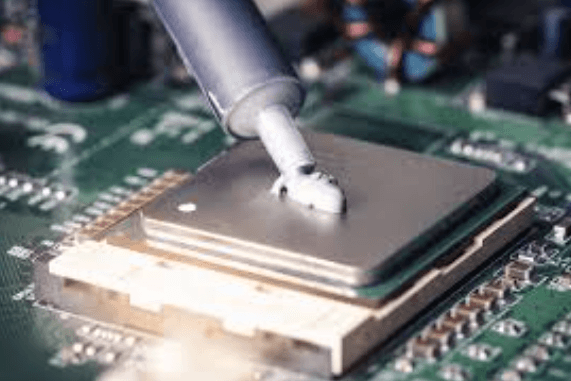
In today’s fast-moving tech world, keeping devices from overheating is more important than ever. Thermal Interface Material (TIM) helps prevent overheating in electronic devices by improving heat transfer between components. Advances in TIM technology continue to enhance cooling efficiency and device performance.
In this blog, we’ll look at the latest breakthroughs in TIM technology and how they help keep our gadgets from overheating. Whether you love tech or work in the industry, you’ll learn about the innovations keeping our devices cool and efficient!
What is Thermal Interface Material (TIM)?
Thermal Interface Material (TIM) is a special substance used to improve heat transfer between two surfaces, usually a heat-producing component (like a processor) and a heatsink. Without TIM, tiny air gaps between these surfaces can trap heat, leading to poor cooling efficiency.
TIM fills these microscopic gaps, allowing heat to move more efficiently and keeping devices from overheating. This helps maintain optimal performance and extends the lifespan of electronic components.
There are various types of TIMs, each designed for specific uses—from smartphones and computers to industrial machines. As technology advances, better thermal management solutions are becoming increasingly important for high-performance devices.
Types of TIMs and their Applications
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) are essential for efficient heat transfer between components in various industries. Different types of TIMs serve specific applications based on performance and ease of use.
1. Traditional TIMs (grease, pads, tapes)
Traditional thermal interface materials (TIMs) have long been fundamental to effective heat management. Commonly used options include thermal greases, pads, and tapes, each offering distinct advantages.
- Thermal Grease: Known for its high thermal conductivity, thermal grease effectively fills microscopic surface imperfections, ensuring optimal heat transfer. However, precise application is required to avoid mess and uneven distribution.
- Thermal Pads: These pre-formed materials provide a uniform thickness and consistent pressure distribution. They are easier to apply than grease, making them a convenient choice, though they may not offer the same level of thermal performance.
- Thermal Tapes: Offering adhesion and heat transfer capabilities, thermal tapes provide a simple, clean, and efficient solution, particularly in mass production. However, their thermal performance is generally lower compared to greases and pads.
Traditional TIMs remain important, but new technologies like phase change materials and liquid metal TIMs are advancing to address their limitations.
2. Advanced TIMs (graphite, phase change materials)
Advanced TIMs are transforming heat management with improved performance and efficiency. Leading innovations include graphite-based TIMs and phase change materials (PCMs), which enhance thermal conductivity and device cooling.
- Graphite-Based TIMs: Graphite-based TIMs offer excellent heat transfer, lightweight design, and durability, making them ideal for compact electronics and industrial applications.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): These materials absorb and release thermal energy by transitioning between solid and liquid states. By effectively regulating temperature fluctuations, PCMs improve device reliability while reducing the need for complex active cooling solutions. This makes them particularly valuable in applications requiring consistent thermal stability.
The synergy between graphite’s robust heat dissipation and PCMs’ dynamic thermal regulation is driving innovation across multiple industries, from consumer electronics to automotive engineering. As demand for efficient and sustainable thermal management solutions grows, these advanced TIMs are set to play a crucial role in shaping next-generation technologies.
3. Emerging TIMs (nanocomposites, carbon nanotubes)
The latest advancements in thermal interface materials (TIMs) are pushing the boundaries of heat management, with nanocomposites and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) leading the way. These cutting-edge materials offer superior thermal properties, outperforming traditional TIMs in efficiency and durability.
- Nanocomposites: By integrating polymers with thermally conductive nanoparticles (such as boron nitride or aluminum oxide), nanocomposites achieve enhanced thermal conductivity while maintaining flexibility and lightweight characteristics. This makes them particularly suitable for compact electronics, wearables, and mobile devices where weight and space constraints are critical.
- Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs): With extraordinary thermal conductivity—often exceeding that of copper—CNTs efficiently dissipate heat while offering remarkable mechanical strength. Their lightweight and nanoscale structure makes them ideal for high-performance computing, aerospace, and next-generation semiconductor applications.
Emerging TIMs enhance cooling efficiency, boosting processing power and device lifespan. Ongoing research may establish new industry standards for advanced thermal management.
Latest Advancements in Thermal Interface Materials
TIM technology is evolving to meet the demands of compact, high-performance devices. Innovations focus on better thermal conductivity, miniaturization, sustainability, and long-term reliability.
1. Conductivity and Thermal Resistance Improvement
- Making TIMs better at conducting heat and lowering resistance is key to keeping electronic devices from overheating. The more effective a TIM is, the faster it can move heat away from important components.
- Newer TIMs, such as metal-based ones, are much more effective than older options like grease or pads. Scientists are also enhancing these materials at a microscopic level to improve heat flow, prevent hot spots, and increase the lifespan of devices.
- As electronics get more powerful, TIM technology needs to keep advancing to handle the growing heat challenges.
2. Miniaturization for Mobile Devices
- As smartphones, tablets, and wearables become smaller and more powerful, efficient TIMs must adapt to tighter spaces while maintaining high performance.
- Traditional TIMs don’t always work well in small devices, so new materials like phase-change materials and nanocomposites are becoming popular. These materials transfer heat efficiently while taking up less space. Some manufacturers are even building TIMs directly into components to reduce layers and improve performance.
- Future advancements in TIMs will be crucial for maintaining device reliability as mobile technology continues to shrink in size but grow in power.
3. Environmental Sustainability
- The shift toward eco-friendly TIMs is gaining momentum as manufacturers seek sustainable solutions.
- Biodegradable and recyclable TIMs help reduce waste and support a circular economy. Bio-based polymers are emerging as a green alternative, offering comparable performance with fewer environmental impacts.
TIM manufacturers are adopting greener materials, optimizing supply chains, and using renewable energy to reduce carbon footprints. With stricter regulations and rising demand for sustainability, they must balance eco-friendly practices with high thermal performance.
Read also: How Tech Support Scams Target Small Businesses and How to Defend Against Them
Challenges & Future Trends in TIM Development
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) are constantly improving to meet new challenges and industry demands. Advancements focus on better heat transfer, smaller designs for compact devices, and more eco-friendly materials.
1. Scalability and Manufacturing Costs
Producing Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) at scale is challenging, as manufacturers must maintain quality while controlling costs. Simple TIMs like grease and pads are easier and cheaper to produce, while advanced options like nanocomposites require costly specialized equipment. Emerging techniques like 3D printing and roll-to-roll processing may help reduce waste and improve efficiency, making high-performance TIMs more accessible.
2. Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is a growing priority in TIM production. Manufacturers are developing biodegradable and recyclable materials to minimize environmental impact. Energy-efficient TIMs improve heat transfer, reducing power consumption and carbon footprints. Ethical sourcing of raw materials is also crucial to prevent resource depletion. With stricter environmental regulations, companies investing in green solutions will have a competitive advantage.
3. Longevity and Reliability
TIMs need to stay effective over time without degrading. High temperatures can wear down traditional TIMs, reducing heat transfer efficiency. Newer materials like phase-change substances and nanocomposites offer better durability and stability under extreme conditions. Improved adhesives and bonding techniques also help extend TIM lifespan by ensuring a secure fit and minimizing efficiency loss.
4. AI & Machine Learning in TIM Optimization
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing TIM development by improving precision and efficiency. AI can analyze large datasets to identify patterns in thermal performance, helping manufacturers refine TIM formulations faster. Machine learning models predict how materials will perform under different conditions, while AI-driven production adjustments enhance manufacturing efficiency and reduce waste. As technology advances, AI will drive further innovation in TIM performance and sustainability.






